Our Sun is a normal main-sequence G2 star, one of more than 100
billion stars in our galaxy.
diameter: 1,390,000 km.
mass: 1.989e30 kg
temperature: 5800 K (surface)
15,600,000 K (core)
The Sun is by far the largest object in the solar system. It contains more than
99.8% of the total mass of the Solar System (Jupiter contains most of the rest).
It is often said that the Sun is an "ordinary" star. That's true in the sense
that there are many others similar to it. But there are many more smaller stars
than larger ones; the Sun is in the top 10% by mass. The median size of stars in
our galaxy is probably less than half the mass of the Sun.
The Sun is personified in many mythologies: the Greeks called it Helios and the
Romans called it Sol.
The Sun is, at present, about 70% hydrogen and 28% helium by mass everything
else ("metals") amounts to less than 2%. This changes slowly over time as the
Sun converts hydrogen to helium in its core.
The outer layers of the Sun exhibit differential rotation: at the equator the
surface rotates once every 25.4 days; near the poles it's as much as 36 days.
This odd behavior is due to the fact that the Sun is not a solid body like the
Earth. Similar effects are seen in the gas planets. The differential rotation
extends considerably down into the interior of the Sun but the core of the Sun
rotates as a solid body.
 Conditions at the Sun's core (approximately the inner 25% of its
radius) are extreme. The temperature is 15.6 million Kelvin and the pressure is
250 billion atmospheres. At the center of the core the Sun's density is more
than 150 times that of water.
Conditions at the Sun's core (approximately the inner 25% of its
radius) are extreme. The temperature is 15.6 million Kelvin and the pressure is
250 billion atmospheres. At the center of the core the Sun's density is more
than 150 times that of water.
The Sun's energy output (3.86e33 ergs/second or 386 billion billion megawatts)
is produced by nuclear fusion reactions. Each second about 700,000,000 tons of
hydrogen are converted to about 695,000,000 tons of helium and 5,000,000 tons
(=3.86e33 ergs) of energy in the form of gamma rays. As it travels out toward
the surface, the energy is continuously absorbed and re-emitted at lower and
lower temperatures so that by the time it reaches the surface, it is primarily
visible light. For the last 20% of the way to the surface the energy is carried
more by convection than by radiation.
The surface of the Sun, called the photosphere, is at a temperature of about
5800 K. Sunspots are "cool" regions, only 3800 K (they look dark only by
comparison with the surrounding regions). Sunspots can be very large, as much as
50,000 km in diameter. Sunspots are caused by complicated and not very well
understood interactions with the Sun's magnetic field.
A small region known as the chromosphere lies above the photosphere.
![]()
The highly rarefied region above the chromosphere, called the corona, extends
millions of kilometers into space but is visible only during a total solar
eclipse (left). Temperatures in the corona are over 1,000,000 K.
It just happens that the Moon and the Sun appear the same size in the sky as
viewed from the Earth. And since the Moon orbits the Earth in approximately the
same plane as the Earth's orbit around the Sun sometimes the Moon comes directly
between the Earth and the Sun. This is called a solar eclipse; if the alignment
is slighly imperfect then the Moon covers only part of the Sun's disk and the
event is called a partial eclipse. When it lines up perfectly the entire solar
disk is blocked and it is called a total eclipse of the Sun. Partial eclipses
are visible over a wide area of the Earth but the region from which a total
eclipse is visible, called the path of totality, is very narrow, just a few
kilometers (though it is usually thousands of kilometers long). Eclipses of the
Sun happen once or twice a year. If you stay home, you're likely to see a
partial eclipse several times per decade. But since the path of totality is so
small it is very unlikely that it will cross you home. So people often travel
half way around the world just to see a total solar eclipse. To stand in the
shadow of the Moon is an awesome experience. For a few precious minutes it gets
dark in the middle of the day. The stars come out. The animals and birds think
it's time to sleep. And you can see the solar corona. It is well worth a major
journey.
 The Sun's magnetic field is very
strong (by terrestrial standards) and very complicated. Its magnetosphere (also
known as the heliosphere) extends well beyond Pluto.
The Sun's magnetic field is very
strong (by terrestrial standards) and very complicated. Its magnetosphere (also
known as the heliosphere) extends well beyond Pluto.
In addition to heat and light, the Sun also emits a low density stream of
charged particles (mostly electrons and protons) known as the solar wind which
propagates throughout the solar system at about 450 km/sec. The solar wind and
the much higher energy particles ejected by solar flares can have dramatic
effects on the Earth ranging from power line surges to radio interference to the
beautiful aurora borealis.
Recent data from the spacecraft Ulysses show that during the minimum of the
solar cycle the solar wind emanating from the polar regions flows at nearly
double the rate, 750 kilometers per second, that it does at lower latitudes. The
composition of the solar wind also appears to differ in the polar regions.
During the solar maximum, however, the solar wind moves at an intermediate
speed.
Further study of the solar wind will be done by the recently launched Wind, ACE
and SOHO spacecraft from the dynamically stable vantage point directly between
the Earth and the Sun about 1.6 million km from Earth.
The solar wind has large effects on the tails of comets and even has measurable
effects on the trajectories of spacecraft.
Spectacular loops and prominences are often visible on the Sun's limb (left).
The Sun's output is not entirely constant. Nor is the amount of sunspot
activity. There was a period of very low sunspot activity in the latter half of
the 17th century called the Maunder Minimum. It coincides with an abnormally
cold period in northern Europe sometimes known as the Little Ice Age. Since the
formation of the solar system the Sun's output has increased by about 40%.
The Sun is about 4.5 billion years old. Since its birth it has used up about
half of the hydrogen in its core. It will continue to radiate "peacefully" for
another 5 billion years or so (although its luminosity will approximately double
in that time). But eventually it will run out of hydrogen fuel. It will then be
forced into radical changes which, though commonplace by stellar standards, will
result in the total destruction of the Earth (and probably the creation of a
planetary nebula).
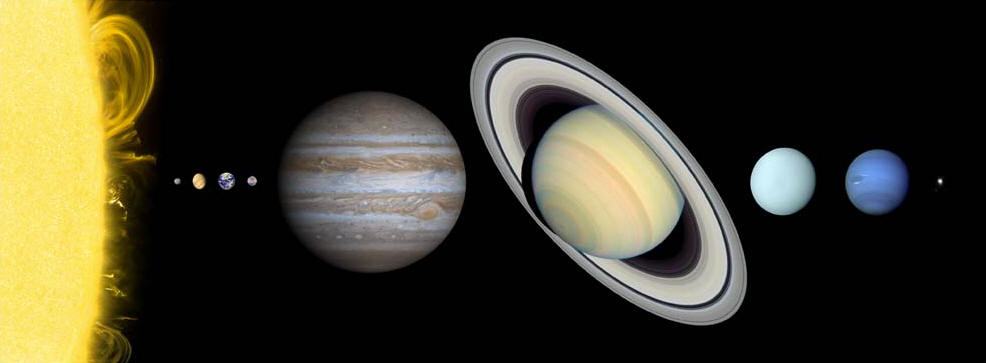
The Sun's satellites
There are nine planets and a large number of smaller objects orbiting the Sun.
(Exactly which bodies should be classified as planets and which as "smaller
objects" has been the source of some controversy, but in the end it is really
only a matter of definition.)
Distance Radius Mass
Planet (000 km) (km) (kg) Discoverer Date
--------- --------- ------ ------- ---------- -----
Mercury 57,910 2439 3.30e23
Venus 108,200 6052 4.87e24
Earth 149,600 6378 5.98e24
Mars 227,940 3397 6.42e23
Jupiter 778,330 71492 1.90e27
Saturn 1,426,940 60268 5.69e26
Uranus 2,870,990 25559 8.69e25 Herschel 1781
Neptune 4,497,070 24764 1.02e26 Galle 1846
Pluto 5,913,520 1160 1.31e22 Tombaugh 1930